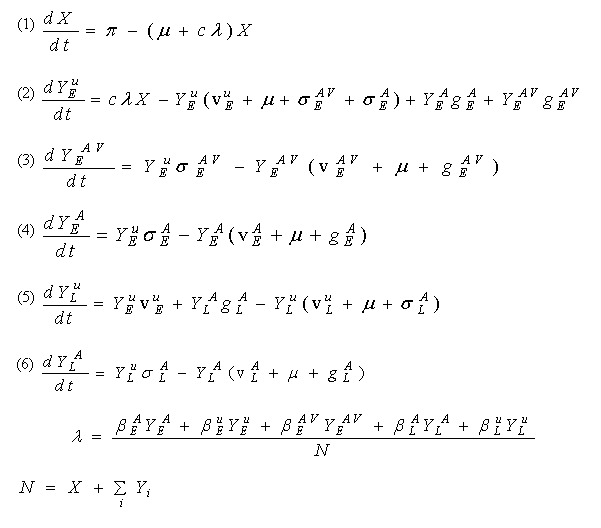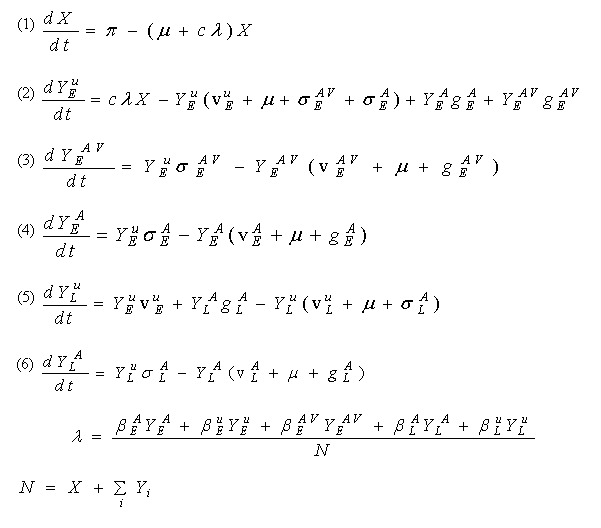
We assumed that individuals join the sexually active population at rate Π and spend an average length of time (1/μ) acquiring new sex partners; during this time period they acquire new sex partners at rate c. The model allowed individuals in the early stages of HIV infection, when they are eligible for the therapeutic vaccine (YEU) to:
Individuals in this eligibility stage can go on and off ARV or on and off ARV plus vaccine. Individuals in late stage HIV-infection (YLU) can go on and off treatment (ARV only). For individuals in the eligibility stage the per capita treatment rate of ARV is specified by σEA, and the per capita treatment rate of ARV plus therapeutic vaccine is specified by σEAV; the per capita rate of giving up ARV per year for these individuals is gEA and gEAV respectively. For individuals in the late stage of HIV-infection, when they are no longer eligible for the vaccine, the per capita treatment rate of ARV is specified by σLA; the per capita rate of giving up ARV per year for these individuals is gLA. We assume that HIV-infected individuals will progress to disease and death at different rates:
We assume that HIV-infected individuals will transmit HIV with different probabilities:
The model is specified by the following equations: